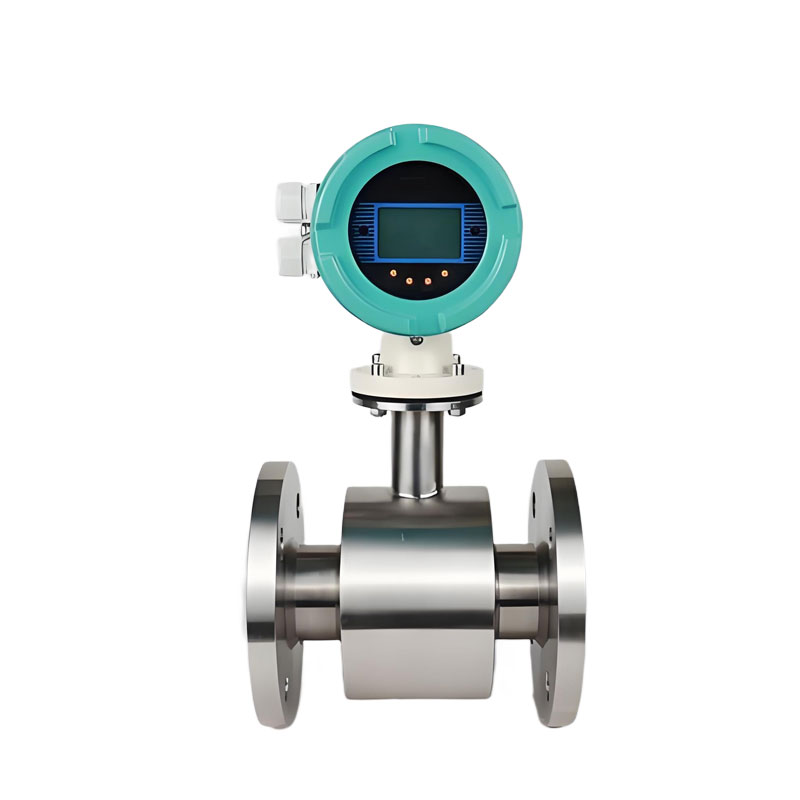
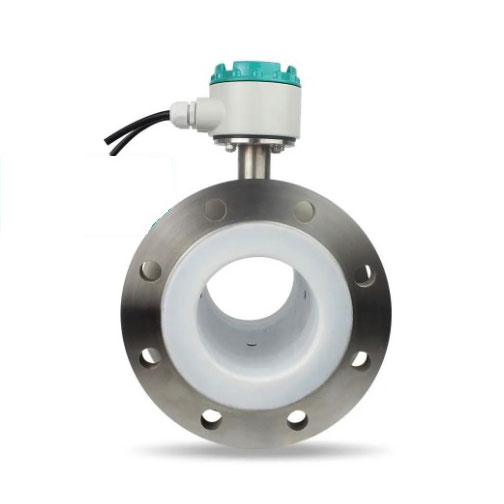
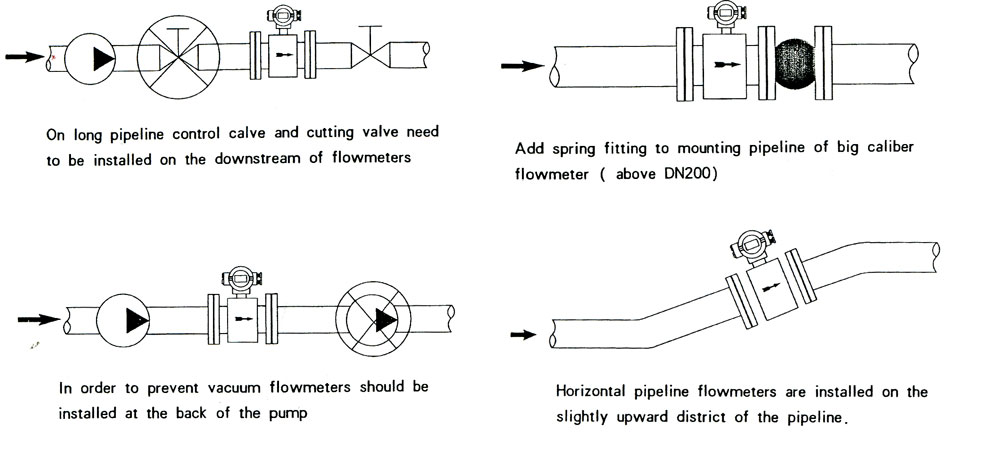
Why Electromagnetic Flow Meters Are Ideal for Vanadium Solution Measurement
If you work with vanadium solutions—like those used in flow batteries, chemical processing, or mining—you know these liquids can be tricky. They’re often acidic, corrosive, and packed with metal ions.
For example, we use
liquid turbine flow meters and
vortex flow meters to measure Vanadium solution. The rotor of the liquid turbine and the probe of the vortex street are made of metal and quickly corroded by Vanadium solution.
Measuring their flow rate accurately without damaging equipment? That’s a challenge. Here’s where electromagnetic flow meters (
mag meters) shine. Let’s break down why they’re a top choice for vanadium solutions.
How do mag meters work for vanadium flow measurement?
Mag meters use Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction. Here’s the simple version:
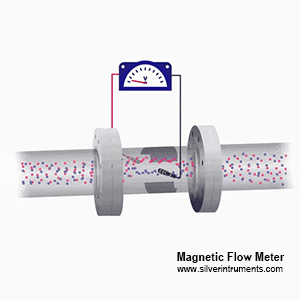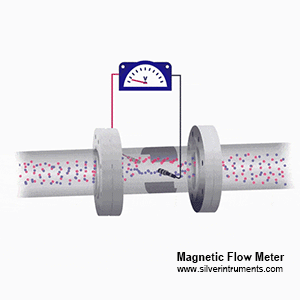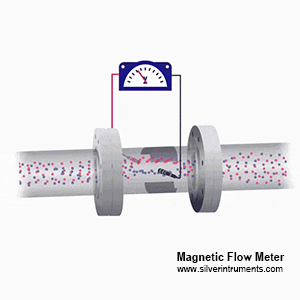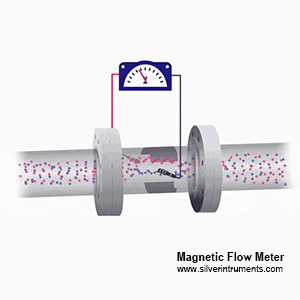
Magnetic flow meter principle
1.When a conductive liquid (like vanadium solution) flows through a pipe, the magmeter generates a magnetic field.
2.As the vanadium liquid moves, it creates a voltage proportional to its vanadium flow speed.
3.Electrodes in the vanadium flow sensor detect this voltage, and the device calculates the flow rate.
Vanadium solutions are conductive because they contain ions (like VO²⁺ or V³⁺), making them perfect for magnetic meters. Non-conductive fluids? Electromagnetic flow meters won’t work. But for vanadium, it’s a match.
Magnetic Flow Meters measure Vanadium Solutions
Why Magnetic Flow Meters Handle Vanadium Solutions Better
1. No Moving Parts to Corrode
Vanadium solutions, especially acidic ones, eat away at metals. Traditional flow meters (like TUF turbine flow meter, vortex flow meters , oval gear flow meters) have metal gears or blades that degrade. Mag meters? They’re just a smooth pipe with electrodes. It is full bore flow meter and without any pressure loss. Less wear, fewer breakdowns.
2. Works with Aggressive Chemistries
Mag meter liners (the part touching the liquid) can be made from materials like PTFE, PFA, or F46 that resist vanadium’s corrosion. Electromagnetic flow meters can be equipped with tantalum material as two electrode materials. Tantalum is a precious metal that has corrosion resistance to many acidic chemical media, such as Vanadium, a liquid with good corrosion resistance. They’ll last many years even in harsh conditions.
3. No Pressure Drop
Full bore flow meter and no pressure loss
Since there’s nothing blocking the flow, mag meters don’t slow down your vanadium solution. That’s critical for processes needing steady flow rates, like vanadium redox flow batteries.
4. Easy Maintenance
No clogs from particles in the solution. Just occasional cleaning of the electrodes (if buildup happens).
Key Specs to Check When Choosing a Mag Meter
Not all mag meters are equal. For vanadium solutions, look for:
-
Liner Material: PTFE or PFA for acidic solutions; ceramic for high-temperature cases.
Here is a table to explain rubber liner and Teflon liner
|
Liner Material
|
Main Function
|
Application
|
|
Hard
Rubber
|
Resistant to Hydrochloric acid, acetic acid ,oxalic acid, ammonia water, phosphoric acid and 50% Sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide in normal temperature
avoid enhancer
|
1. Temp. less than 65 °C
2. Common acid, alkali, salt solution
|
PTFE
F46
PFA
|
Most steady plastic of chemical living energy; resist boiling hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, nitro- hydrochloric acid, thick alkali and all kinds of organic solvent;
Poor abrasion and adhesion performance
|
1. -40°C ~130°C(PTFE)
-40°C ~180°C(F46)
-40°C ~180°C(PFA )
2. Strong corrosive fluids such as acid and alkali
3. For sanitary purpose
|
-
Electrode Type: tantalum for corrosion resistance.
Tantalum has good performance of resisting erosion, similar to glass; Besides hydrofluoric acid, fuming nitric acid, alkali, nearly can resist erosion of all chemical mediums(including boiling hydrochloric acid, vanadium ,nitric acid and below 150℃ sulfuric acid ). Not resisting erosion in alkali.
-
Accuracy: ±0.5% is standard, but some go down to ±0.2%.contact silverinstruments.com if you want to Customize the high-precision flowmeter you need.
-
Temperature Range: -4°F to 356°F (–20°C to 180°C) covers most vanadium applications.
-
Pipe Size: From 0.1” to 40” diameters—pick one that fits your system.
Below is flow range table for different vanadium flow range corresponding to different magnetic flow meter size
Mag flow sensor size
|
Mag flow sensor size
(mm)
|
Vanadium Flow Range
(m3/h)
|
DN15 (1/2 inch)
DN20 (3/4 inch)
DN25 (1 inch)
DN32 (1-1/4inch)
DN40 (1-1/2 inch)
DN50 (2 inch)
DN65 (2-1/2 inch)
DN80 (3 inch)
DN100 ( 4 inch)
DN125 (5 inch)
DN150 (6 inch)
|
0.06~6.36
0.11~11.30
0.18~17.66
0.29~28.94
0.5~45.22
0.71~70.65
1.19~119.40
1.81~18.086
2.83~282.60
4.42~441.56
6.36~635.85
|
If you need to measure lower vanadium flow range (low flow rate flow meter ) , or higher flow measurement, silverinstruments.com has solutions.
Real-World Example: Vanadium Flow Batteries
In vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs), two vanadium electrolyte solutions circulate through the system. Mag meters here track flow rates to optimize energy efficiency. If the flow is too slow, the battery underperforms; too fast, and you waste pump energy. Mag meters provide precise control, ensuring the sweet spot.
How to install vanadium solution flow meter
A Few Limitations? Sure.
Mag meters need conductive liquids (vanadium solutions qualify). They also require a minimum flow speed (~0.3 ft/s) to work accurately. But for most industrial setups, these aren’t dealbreakers.
If you're moving vanadium solutions, electromagnetic flow meters offer a reliable, low-maintenance solution. They handle corrosion, avoid pressure loss, and deliver precise data—critical for industries where vanadium’s reactivity can’t be ignored. Just match the meter's specs to your solution's pH, temperature, and ion concentration, and you're golden.