Vanadium Solution Flow Meter (Magnetic): Materials, Sizing & VRFB Applications
Why mag meters are ideal for vanadium electrolyte
- No moving parts → no rotor/blade corrosion like turbine flow meters or vortex flow meters.
- Full-bore design, near-zero pressure loss → stable circulation in VRFB stacks.
- Excellent chemical resistance with PTFE/PFA liners and tantalum electrodes.
- Works on conductive liquids — vanadium electrolytes (VO2+, V3+ etc.) are conductive, so mag meters read accurately.
How an electromagnetic flow meter measures vanadium flow
Mag meters follow Faraday’s law. When conductive vanadium electrolyte passes through a magnetic field, electrodes sense a voltage proportional to flow velocity, and the transmitter outputs volumetric flow.
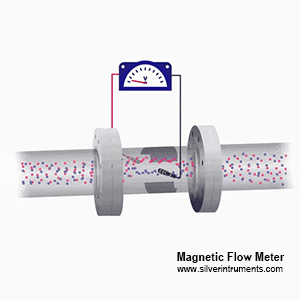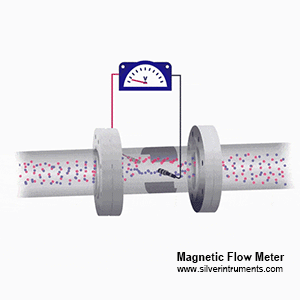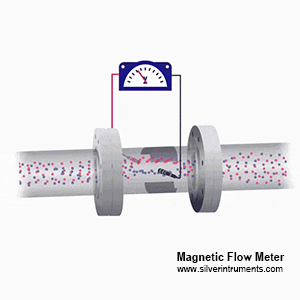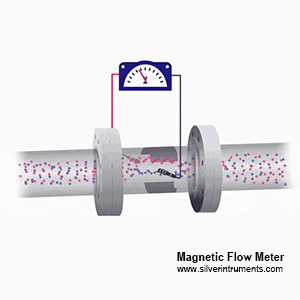
For non-conductive media (e.g., some solvents), mag meters won’t work — consider Coriolis mass flow meters or ultrasonic alternatives.
Material selection for vanadium solutions
Liner materials (PTFE / PFA vs. rubber)
Choose liners based on acidity, temperature, and solids. For V(II)–V(V) electrolytes (often acidic), PTFE / PFA are preferred. Rubber is acceptable only for mild conditions.
| Liner | Main properties | Recommended applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hard rubber | Resistant to common acids/alkalis at room temperature; not for strong oxidizers | Temp < 65 °C; general acid/alkali/salt solutions |
| PTFE / F46 / PFA | Outstanding chemical inertness; resists boiling HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, mixed acids; poorer abrasion resistance | PTFE: −40~130 °C; F46/PFA: −40~180 °C; strong corrosives, sanitary service |
Electrodes (tantalum recommended)
Tantalum behaves like glass in corrosion resistance: withstanding boiling HCl, nitric acid, and vanadium electrolytes; not suitable for strong alkalis. For cost-sensitive use, Hastelloy or titanium may be considered depending on chemistry.
How to size a vanadium solution flow meter
Target a typical velocity of 0.5–3 m/s for accuracy and low erosion. The table below shows approximate ranges at standard calibration; confirm with your actual velocity window.
| Mag flow sensor size (mm / inch) | Typical vanadium flow range (m³/h) |
|---|---|
| DN15 (1/2") | 0.06–6.36 |
| DN20 (3/4") | 0.11–11.30 |
| DN25 (1") | 0.18–17.66 |
| DN32 (1-1/4") | 0.29–28.94 |
| DN40 (1-1/2") | 0.50–45.22 |
| DN50 (2") | 0.71–70.65 |
| DN65 (2-1/2") | 1.19–119.40 |
| DN80 (3") | 1.81–180.86 |
| DN100 (4") | 2.83–282.60 |
| DN125 (5") | 4.42–441.56 |
| DN150 (6") | 6.36–635.85 |
Accuracy: ±0.5% standard; optional ±0.2%. Temperature: −20~180 °C (liner-dependent). Pipe sizes: 0.1"–40".
If you require very low flow or high-range measurement, we can customize transmitters and liners for your electrolyte.
VRFB application example

In VRFB systems, two vanadium electrolytes circulate through cell stacks. Mag meters maintain the optimal circulation rate: too slow lowers power output; too fast wastes pump energy.
Installation tips for vanadium solution flow meters
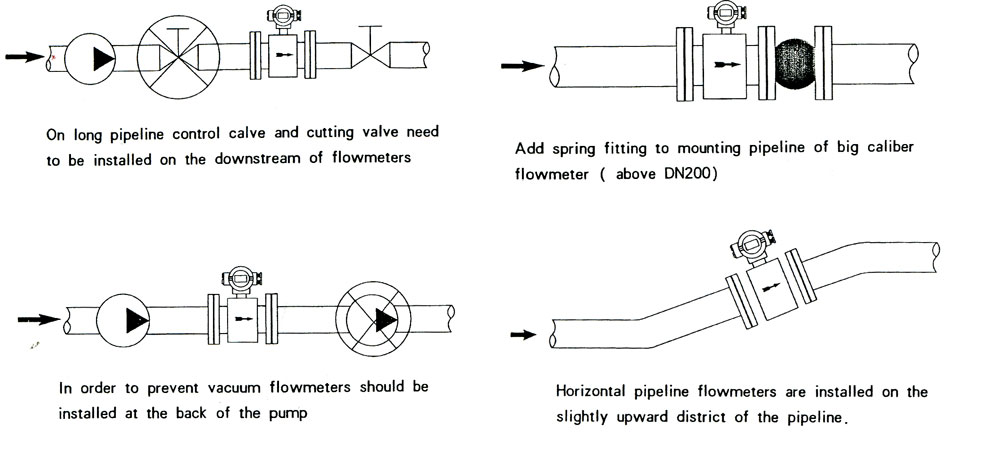
- Keep straight runs (e.g., 5D upstream / 3D downstream) or follow your model’s spec.
- Ensure full pipe; avoid gas pockets. Install with electrodes on a horizontal line.
- Use proper grounding rings; choose PTFE/PFA gaskets compatible with the electrolyte.
Limitations
Mag meters require conductive liquids and a minimum velocity (~0.3 ft/s) for best accuracy. For non-conductive solvents, consider Coriolis or ultrasonic meters.
Need a Vanadium Electrolyte Flow Meter?
Silver Automation Instruments supplies PTFE/PFA-lined mag meters with tantalum electrodes for VRFB and chemical services, plus options for low-flow, high-temperature,
and sanitary applications.
Explore magnetic flow meters
Vanadium Flow Meter FAQs
Which electrode material is best for vanadium electrolyte?
Tantalum is recommended for strong acidic electrolytes; avoid strong alkalis.
What velocity should I design for?
Typically 0.5–3 m/s balances accuracy and erosion control in VRFB loops.
Will mag meters cause pressure loss?
They are full-bore; pressure loss is negligible compared with turbine/vortex meters.

















 English
English  français
français  Español
Español  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  tiếng việt
tiếng việt  Türkçe
Türkçe  ไทย
ไทย  українська
українська  Malay
Malay  עברי
עברי  Indonesia
Indonesia  Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα  ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ  հայերեն
հայերեն 



 Email
Email
 WA
WA
 Inquiry
Inquiry
