Thermal mass flow meters and ultrasonic flow meters are both widely used in industrial compressed air metering. The choice between these two options directly affects the accuracy of energy consumption monitoring, operation and maintenance costs, and production stability. In this article ,we have compared the two technologies by examining their operating principles, key performance characteristics, as well as installation and real-world usage considerations. We also walk you through a practical how-to guide to help you select and implement the right solution.

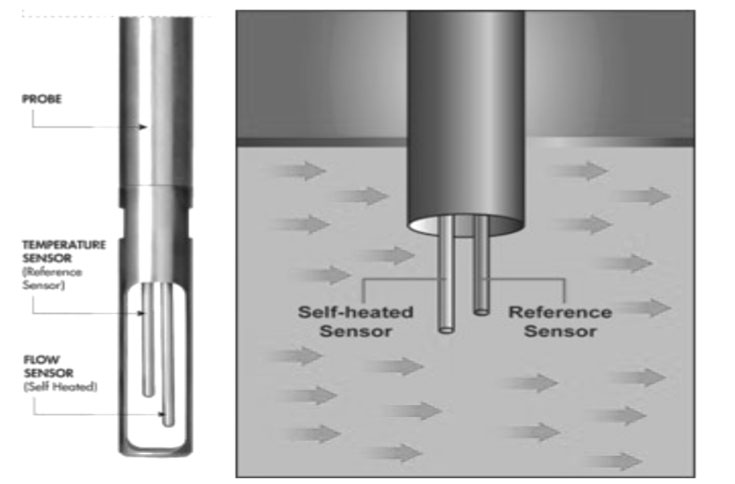
1. Thermal mass flow meter principle
2. Ultrasonic gas flow meter principle
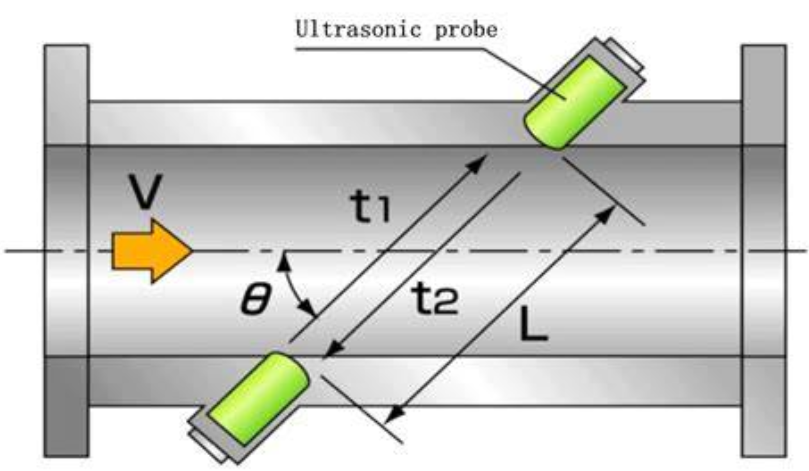
Ultrasonic flow meters for air mainly use the Time of Flight method, which emits sound waves through paired transducers upstream and downstream, and calculates the flow velocity using the time difference between forward and backward propagation. Ultrasonic type compressed air flow meter is designed for non-contact air flow measurement and even without cutting the pipelines when install the air flow sensor, with no moving parts inside the pipeline, and is suitable for complex working conditions with large diameters and high pressures.
The core of selection is to match performance parameters with actual operating conditions. The following table clearly compares the key performance indicators of the two types of flow meters, covering core dimensions such as accuracy, range ratio, pressure resistance, and heat resistance:
|
Performance Indicators |
Thermal Compressed Air Flow Meters |
Ultrasonic Compressed Air Flow Meters |
|
Measurement Accuracy |
±1%FS, high-precision models up to ±0.5%FS |
General type ±1%~±2.5%, high-precision type ±0.5%~±1% |
|
Flow Range Ratio |
Typical 10:1~20:1, suitable for small and medium flow fluctuations |
20:1~40:1, significant wide-range advantage, suitable for large flow fluctuations |
|
Pressure Resistance Range |
Regular ≤1.6MPa, custom models up to 4MPa |
Regular ≤10MPa, suitable for high-pressure industrial pipelines |
|
Signal Output |
Supports 4-20mA current signal, pulse signal, some with RS485 communication |
Standard 4-20mA signal (accuracy 0.1%), expandable with wireless transmission module |

The installation standardization of thermal flow meters directly affects measurement accuracy, and the core follows the principle of "reserved straight pipe section+correct insertion depth". The insertion type thermal mass flow meter for air requires insertion into the axis of the pipeline, and the length of the measuring rod is customized according to the pipe diameter. If it cannot be fully inserted, the manufacturer needs to provide calibration coefficients to compensate for errors.
Insertion thermal mass flow meter:
1. Selection: Straight pipe sections are needed before and after flow meter, with upstream reserved straight pipe sections of ≥ 10 times the diameter (10D), downstream reserved straight pipe sections of ≥ 5D, avoiding disturbance sources such as elbows and valves;
2. Fixed base when install insertion type mass flow meter: The base (which is normally provided by supplier like silverinstruments.com) is welded to the top of the pipeline, ensuring that the axis of the through-hole is perpendicular to the axis of the pipeline;
3. Sealed connection: When installing a dedicated ball valve, nylon gaskets should be used for medium temperatures below 100 ℃, and copper gaskets should be used for temperatures above 100 ℃. Loctite 567 pipe thread sealant can be used for sealing;
4. Thermal mass flow probe installation: Loosen the retaining nut, insert the probe into the pipeline to the positioning position (the probe is normally in the middle of the pipeline), rotate the connecting rod to align the arrow with the flow direction, and tighten the nut;
5. Electrical connection for digital thermal mass flow transmitter: Connect the 4-20mA signal line according to the instructions manuals from silverinstruments.com, and ensure proper shielding and grounding to avoid electromagnetic interference.
In-line thermal mass flow meter installation:
Inline type thermal flowmeter is easier to install comparing to insertion type thermal mass flow meter, and it is pre installed in a dedicated pipe section before leaving the factory. Simply connect the pipeline according to the flange standard (GB/T9119-2000) to ensure that the pipeline axis is horizontal with an error of ≤± 2.5 °. However you should straight pipeline before and after flow meter as insertion type flow meter.

The installation core of ultrasonic flowmeter focuses on "transducer layout+reserved straight pipe section+signal shielding". The time difference method model needs to ensure symmetrical installation of upstream and downstream transducers, and the angle between the sound wave propagation direction and the pipeline axis meets the manufacturer's requirements. The specific operational points include:
1. Straight pipe section: Reserve a straight pipe section of ≥ 10D upstream and ≥ 5D downstream, and extend it when approaching the disturbance source;
2. Installation of transducers: V and Z methods can be used for arrangement to ensure that the sound wave propagation path is unobstructed, and the installation surface needs to be polished flat;
3. Electrical protection: The 4-20mA signal line and power line are laid separately, the shielding layer is grounded at one end, and the impedance matching is 0-1KW;
4. Debugging and Calibration: After installation, parameters such as pipe diameter and wall thickness need to be input to optimize measurement accuracy through on-site calibration.
During online installation, a dedicated punch can be used to achieve non-stop operation. During shutdown installation, it is necessary to ensure that the drilling axis is concentric with the base. If the deviation is too large, the aperture can be expanded to reserve adjustment clearance.For small and medium-sized pipe diameters ( such as 1/8” size, 1/4” size or 1/2” size) and high-precision small flow measurement (such as in laboratories and pneumatic branches), thermal flow meters/controllers are preferred.
Ultrasonic flow meters have more advantages in large-diameter pipelines (DN80 or above), high-pressure working conditions (>4MPa), or industrial sites with severe vibration (such as compressor outlets). The design without moving parts can reduce maintenance frequency.
In energy consumption monitoring scenarios, if direct acquisition of mass flow data is required, thermal models are more suitable; If multiple gas metering or high flow fluctuation conditions need to be taken into account, the wide range bit rate of ultrasonic flowmeter is more practical.However, non-contact ultrasonic air flow meters are very expensive, so budget is also a key consideration for customers.
The common fault of thermal flow meters is "measurement drift", which is often caused by probe contamination or insufficient straight pipe section. Cleaning the probe and readjusting the installation position can solve the problem; If there is no signal output, check the power supply and 4-20mA circuit for continuity. If the ultrasonic flowmeter displays "weak signal", it is mostly due to the installation deviation of the transducer or the presence of bubbles in the pipeline. Adjusting the transducer angle or exhaust can restore normal operation.
When the moisture content of compressed air is too high, the thermal sensor is prone to condensation, which affects its accuracy and requires the installation of a drying device; Ultrasonic flow meters need to pay attention to insulation to avoid frost on the inner wall of the pipeline blocking the propagation of sound waves.